The following is our Q&A Section answering many questions that we have received over time. If you have any additional questions, please send them to: ckirmuss@frontier.net
We have spent 9 plus years in researching all past and current processes and methods to clean records. In fact, we found that most if not all processes only focus on cleaning the record’s surface. SOME 40 AND 120 KHZ ULTRASONIC MACHINES ADVERTISED AS ULTRASONICS AFTER OUR TESTING WITH ALUMINUM FOIL AND USING A CAVITATION METER DO NOT USE CAVITATION, DO NOT CAVITATE!
Using the universally recognized aluminum foil test, discovered where some of these machines made in Germany and in the Baltic States and Hong Kong ARE SONIC BUBBLERS. FURTHER VERIFIED BY A CAVITATION TESTER. These are Surface Cleaners at best.
As to cleaning action: The Tribelectric Table of Charges proves where even using an ultrasonic cleaning process, one cannot reach down into the groove as the record is repelling any action. Both record, and water, with or without a soap, repel each other. Further complicating any efforts to clean a record.
Cleaning solutions used see water droplets of 100 to 110 microns in diameter are also an issue, as record grooves are smaller in size.
As such: Many processes have been designed without understanding how records are made, their composition, and how various cleaners or processes may affect the records themselves. No one uses microscopic analysis or signal analyzers to evaluate their process.
In ultrasonic design, seems where no one understands that PVC repels water, where we need to remove oils and contaminants that are 3 to 5 microns in size, and the like.
>>>AS TO RESULTS: Exclusively no one speaks about “db signal gain” or "increase in frequency response" after a cleaning. This is as most processes just surface cleans at best. Air, vacuum, or spin drying a record leaves films on the surface of the record. We restore the grooves!
Below is an image of fungus on a record’s surface and groove left over after cleaning by an advertised 40 KHz ultrasonic at 4 times the price of the KA-RC-1. Fungus removed but not the dust held in the groove by the record's release agent. In fact, this 40 KHz sonic is actually a sonic bubbler, and does not use cavitation. It just agitates the soap used in the water basin. Whatever came off the record's surface was air dried back onto the record. In this case the so called filter has pores that are 300 microns average in size. No filtration!
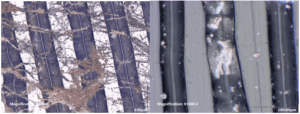
We designed our process to apply an ionizing spray to change the charge of the record to attract cavitation. First cycle of the record placed in our machine sees us so a surface clean. Removing first films left over from prior cleaning processes.
As the record spins, the induced charge to attract the effects of cavitation "washes off". So we reapply the spray, another cycle in the machine, this time we continue to remove these films as some cleaning solutions severely coat the record and as we proceed, we then also remove the film deposited on the record while the record had been trapped in its sleeve, upwards of many decades. (Outgassing of the plasticizer).
As the record spins for another cycle, the record returns to its original charge. Needed another cycle or two. We now finally remove the release agent that surfaced during the pressing process. This "Pressing oil" allows the record to "pop out" of the stamper. BEFORE KIRMUSS PROCESSING, your needle is making contact with these contaminants. Music hidden" RESTORING the record, fused in dirt and dust landing on the cooling record at the pressing plant, cause where those nasty pops and clicks reside, heard in new and vintage records, also now removed.
A Kirmuss processed record needs no air, vacuum or spin drying. It comes out virtually dry! PROOF OF THE KIRMUSS RESTORATION PROCESS. Further: The Tribelectric Table of Charges mentioned above where PVC repels water.
To assure even cavitation, our patented process assures the records are suspended at the proper height irrespective of the record size without damaging the label and not to overload the ultrasonic and diminishing the effects of cavitation.
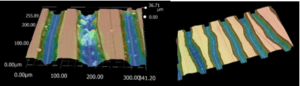
The above image shows the same grooves BEFORE and AFTER the Kirmuss Restoration Process. Contaminants and residues from prior cleanings are removed first, then the release agent that has captured dirt, dust, etc. causing those unwanted pops and clicks.
We use safe a 35 KHz ultrasonic frequency and to avoid standing waves that reduce efficiency, we add a 70 KHz passive resonance. We make changes as to the resonant frequency so we are not just a 35 KHz look alike. This evens out cavitation. In fact, using the aluminum foil test, and with a Cavin cavitation meter, where we produce 810 Cavins of sonic energy, Our 4 records spaced properly with the resonance added evenly distributes the cavitation from bottom to top of the tank and where we do not create high energy impacts onto the record. The Patents Pending record spacing and suspension system sees records now float and are not skewered, keeping record labels dry and not damaging them as with other processes.
Proper frequency, proper size (and velocity) of the cavitation bubble, resonance to even out the "violent result of cavitation", and record ionization and proper spacing results in the record being restored from the record's edge up to the needle removal point of the record. (dead wax area).
No continuous running heaters are used and where we monitor water temperature.
With only a few water droplets left: the proven over time mechanical drying and groove polishing method with the supplied soft lint free optician's cloth is used. No films are therefore left.
RECORD RESTORED!
YOUR NEEDLE DISCOVERS THE DETAIL HIDDEN OF THE PRESSING, even in new records!
PVC Friendly, water soluble, 98- 99% Distilled Water and 1% - 2% Diol2 Propandiol 178, a type of propanol.
Our mix is both anti-static and anti-fungal. It is PVC friendly and water soluble. This is also needed to be sprayed onto the record as PVC in records rejects and repels water by its nature; the surfactant acts as a “wetting agent”, reducing surface tension and thus helps attract, for lack of a better term, the resulting 500 MPH plasma wave that results from the cavitating and exploding micro-bubbles in the tank. It "changes the respective charge of the record with the water in the tank".
With the supplied surfactant brushed into the record’s grooves, this therefore assists in the cleaning action in the grooves.
A bath with distilled water alone or with a cleaning agent in an ultrasonic’ s tank added will not do anything to clean the grooves, it just lightly cleans or wets the surface.
Keep in mind that WE RESTORE GROOVES and not just clean the record's surface..
AS TO 5 MINUTE CYCLES OR 2 MINUTE CYCLES.. USE 5 MINUTE CYCLES PER THE MANUAL...You will see a rise and fall usually of a whitish material appear, this is the colorant in the spray that shows what the ultrasonic has pulled off the record. last cycle where this disspates quicky.
BUT: If the record sees after the first application of surfactant and taking the record out of the machine and after a tap to remove water and when the record is placed horizontally on the work area the appearance of thousands of little beads of water, or where there is a sheeting of water at the bottom of the record this indicates where a coating was applied to the record. This impedes the action of our ionizing surfactant agent to attract the plasma wave into the record’s grooves, so one would then have to switch to a FIXED operation irrespective of what you see coming out of the record. (Note: always pad dry the goat hair brush between applications of the ionizing spray). MODIFIED PROCEDURE, when you see this sheeting of water or working with records that are 16 years or younger: After the first 5 minute cycle with spray applied, use four 2 minute cycles with a final 5 minute cycle with spray applied. Between cycles use the supplied rabbit cloth to recove any water on the record. These records will leach always. (with water on the record the ionizing spray is not doing much as it is being diluted with the water.
In most cases, the record should come out of the machine with little water at the end. DO NOT LOOK FOR THE RAPID DISSIPATION OF THE COLORANT. You have restored the record. In all cases: before applying the ionizing surfactant spray, use the rabbit cloth to wipe off the water on the record before the application of the ionizing agent.
Usually when dealing with records usually a record that has not been abused or coated with an aggressive cleaner we will see 3 to 5 minute cycles of five minutes.
>>>We have found Mofi and Acoustic Sounds records (new ones) as also having a severe coating on them, as well as records that were coated with LAST protectant as well as cleaned with L’Art du Son and VPI’s cleaner. USE the suggested four 2 minute cycles after the first 5 minute cycle with spray applied, followed by a final 5 minute cycle. .
Also per the manual: Pad dry the goat hair brush with the rabbit cloth the goat hair brush between applications of ionizing spray; this removes picked the colorant that we see that may have been accumulated by the brush. This before every application.
The short answer as to vinyl records is NO.
Photoflow which is used in the development of print film and paper repels water which is exactly the opposite of what we are trying to accomplish. Per KODAK: “decreases water-surface tension and minimizes water marks and streaks on film to promote faster and more uniform drying.” In a photographic washing process you want to see water run off the paper or film when it is drying to avoid water spots. Photoflow is added to the water in the wash cycle. Sonic cleaning systems need to see anything making contact with the record to attract the plasma wave to aid in the cleaning process. Adding Photoflow decreases the effectiveness of any surfactant applied on a record’s surface.
Studies have shown where high amounts of alcohol affect the plasticizer of the record, damaging the record over time. There are many published lists of how various agents affect or do not affect PVC.
- Shellacked records cannot tolerate alcohol unless it is found in the ratio of our system. (For these records we brush in surfactant and only see one 2 minute cycle used).
2. The distilled water with the 1.4 ounces of 70% isopropyl alcohol as we recommend does not aid in the deep cleaning and restoration of record grooves. 70% or less is soluble in water, (90% is not = danger!).. We use in the first 2 or 5 minute cycle the bath with no ionizing surfactant brushed into the the record's grooves just to first wet the record and remove any fingerprints and dust, dirt, that may be on the record’s surface. The 1.4 ounces of 70% IPA is primarily used to kill fungus that is alive or dormant that falls to the bottom of the basin.
NEVER USE 70% RUBBING ALCOHOL: It has additives for skin care and is not to be used.
You can clean AND RESTORE two 33 1/3, one 45, and one 78 at the same time. The spacing between the records is crucial to the process, any larger number of record within the same space reduces the advantage of the ultrasonic that works the surfactant into the record grooves.
One 2 minute cycle to surface clean. Multiple 2 or 5 minute cycles with the ionizing surfactant to RESTORE.
To the bath: We suggest you change out the distilled water with the 1.4 ounces of 70% IPA in the tank after restoring between 15 to 20 records or when the water becomes murky. Severely contaminated records will show up with murky water in the tub. Do not let the water stand in the restoration system overnight. It will grow fungus once the alcohol has evaporated.
Please discard.
You should be able to clean between 25 and 40 records before requiring a new spray bottle. (60 mL). The number of applications depends on the number cycles that you require to restore the record. Six cycles would see less records restored, around 20.
The cost is reasonable: Between 28 and 38 cents per record. Varies based on the number of cycles.
Once a record has been restored, we do not need to process a record with the cycles as described. A two minute cycle is suggested when one feels the record needs to be "surface cleaned", as no matter how careful we are, we will always leave fingerprints and the like on the record as we handle it.
Many cleaning agents used on records are aggressive and actually "shine" the record, leaving a hard to remove coating. A shiny record is not indicative of a restored record. One cleaning solution sold sees one have to use 6 or 7 five minute cycles. Consuming more ionizing spray.
To note there is a colorant in the spray that allows one to see what the ultrasonic "pulled out" of the record's grooves in the prior cycle. This aids in determining when a record has been restored. A virtually dry record is also indication of the end of process.
Also available: a 300 mL refill bottle. This is approximately 20% lower in cost per serving.
The Tribelectric Table of Charges states where PVC and water, with or without soap, repel each other. A restored record sees this. That is why we do not need air, vacuum or spin drying of a processed record. We cannot say this for other cleaning systems and processes.
In our studies of record washing programs and methods it has been very evident in our research where many sonic systems do little to the record other than surface shining. As the records are "still wet", these machines blow room air onto the record by way of a fan after being processed ultrasonically. This sees one air dry onto the record whatever contaminants were left in the ultrasonic bath. Noted and tested where in tank water filters supplied by some manufacturers in fact do not filter out dirt, dust and fungus, these are between 3 and 5 microns in size. These reside in the water that one is air drying onto the record. The more records processed, more contaminants left in the tank. This defeats the purpose of cleaning a record, one would think. Added, the fan itself blows dust onto the record and moving air also adds a static charge to the record. These both cancel out entire effort to clean the record!
As to vacuum drying: Vacuum drying brings through the Venturi Effect surrounding dust back onto the record. While the vacuum sucks off water from the enzyme cleaner (many of which are not PVC friendly) this process does not go into the grooves and does not remove all of the residues left of the cleaning agent and process. Moving air also charges the record, creating an issue of static.
OUR RECORDS AFTER PROPER PROCESSING COME OUT VIRTUALLY DRY.. This as per the Tribelectric table of charges, water and PVC have the same charge and they repel each other. Thus to remove the remaining water droplets on the record, we use the tried and true mechanical method.. using a lint free optician’s cloth as well as the use of a parastatic felt brush by mechanical means to further polish the grooves. A little elbow grease goes a long way!
Other systems and cleaning methods see pools of water remain on the surface of the record as they have not been properly cleaned. That is why they use blowers and vacuums, but the latter defeats the purpose of cleaning a record and leaving a film on the record by so doing.
Firstly, anyone that advertises that they have an effective filter to clean water in a sonic bath or tank as in other laboratory grade equipment is fooling the buyer.
Below is a picture of a filter used in a $5,000 ultrasonic record washer. Measurement taken by our 2D/3D microscope.

Fungal spores found on records are 1- 3 microns (µm) in size. Depending on the spore. They end up in the reservoir of the ultrasonic system. After analysis, the filter in this very expensive machine cannot filter out anything less than 143-160 microns (µm). To note where sand ( particle size > 63 µm ), silt (particle size > 2 µm), dust (particle size 0.5 to 100 µm, all pass through the supplied filter of this very expensive machine and return to the water in the tank. They are using a $2.00 foam filter. This manufacturer also asks one to keep the water in the tank and replace it every 100 records. Fungus grows in stagnant waster! That is why we sometimes need to process a record for 6 or 7 five minute cycles as we have to strip out these remnants of prior cleaning processes that rely on air drying that are “baked” onto the record.
To your question: we therefore ask you change the water out every 15 or so records.
Records by their nature repel water so when we do the final 5 minute cycle with the sonic and surfactant, we then remove the record and then with the record mounted at our work station horizontally, mist very lightly the record with distilled water at 12, 4 and 8 o’clock positions. We then rely on our mechanical process of using an optician’s cloth to dry the surface and then use the parasitic felt brush to polish the grooves.
In our process we therefore provide 1.5 to 5 dB gain to your phono stage.
Frequency is key, we use 35KHz.
The Higher the frequency, the higher the speed of the resulting plasma wave from the cavitating microbubble. On the opposite end, 25 KHz is too low a frequency to provide any effective cleaning of a record’s groove, plasma wave is too slow. 125, 190 KHz, not to be used!
To note where there are other elements to consider when selecting an ultrasonic based system:
Temperature is critical: Ultrasonic bubbles create heat when they cavitate (burst), thus water in the tub of any sonic used should not exceed 95 deg F. Our system allows you to see the progression of this heat generated by the cavitation process. We signal a visual alarm.
What is in the tank is also critical: in our process we use no enzymes, no non PVC safe materials, only water soluble surfactants. Many systems use high concentrations of alcohol which damages the plasticizer of the record. Others see the creation of more fungus with enzyme based agents.
Systems with tanks that keep water for more than a day should be avoided, as fungal spores are omnipresent, causing health risks.
We recommend where the water in our tank is not kept for more than one day.
Every manufacturer should have available a certificate in their name from a qualified testing laboratory that meets with local electrical and safety requirements. You should see a UL or CSA or local electrical authorities testing label on the product, for your safety against shock and fire, as well as an FCC Part B Compliance statement.
DIY systems see contraptions that hold the records which can be dangerous if they fall into the water with a potential for electrocution.
Our system is ETL Tested against UL, CSA, PSC, and CE with FCC certification.
With any system and in stating that a record is clean in 5 minutes or 10 minutes is not accurate. In fact it is arbitrary. Is it Clean? Some ultrasonic systems need severely contaminated records to be washed repeatedly for 60-90 minutes and still not having the expected results commensurate to the time spent. In our process we allow one to see first hand when the record has been restored.
After every 5 minute cycle using our surfactant applied to the surface of the record, we keep applying this to the record by way of brush and between applications until there is a noticeable decrease in the presence of a white paste-like substance while the brush is used. Or rapid evaporating of this materials. This is validation of our restoration action stripping out fungus and contaminants not removed by other systems or processes.
Very hard to give you an exact number as one does not now the provenance of the record and how it was maintained. usually we see three or four, maximum five, 5 minute cycles. We see a rise and fall of a whitish colorant as described appear, then dissipate as we brush the ionizing agent onto the record. This shows what the sonic "pulled off" the record in the previous cycle. Records as we process them have less and less water visible as we near the end. SOME RECORDS, processed with L"Art du Son, Disk Doctor and other aggressive cleaning agents will always stay wet, or will always see this whitish colorant appear. In general, we see new records have severe coatings on them: we now recommend for any new record pressing to modify the baseline instructions: After the first 5 minute pre-wash cycle, use a 5 minute cycle with ionizing spray applied, then follow with four 2 minute cycles of spray applied, then a final 5 minute cycle with the ionizing surfactant applied. We will NOT look at what we see as to the colorant or the amount of water found on the record. FIXED TIME to the process. We will strip out in records where LAST was applied (noted by hundreds of water droplets visible on the record) using the 5 (5-2-2-2-2-5) process. FIXED TIME. >
With other records following the manual and technical supplements, , we on average see 3 to 5, five minute cycles with corresponding application of the ionizing agent applied.
Users that have cleaned their records in a prior ultrasonic cleaning system using a fan to air dry and where the water has not been changed for months, or for a tank that managed 100 records, sees us repeat our cycle 6 or 7 times.
With records cleaned prior with vacuum systems, 4 to 5 five minute cycles are common.
The above is not the fault of our process, it is a result of the record being improperly cleaned using another process.
Note where other ultrasonic processes and even ours where one tries to keep records spinning in distilled water with or without a soap added to the water for hours, this cannot clean a record properly. An ionizing agent must be applied to the record over several cycles to see the charge of the record change to be opposite to the charge of the distilled water. Multiple cycles as we describe are needed as the charge of the record returns to that of the water, nullifying therefore the advantages of the ultrasonic. Using the system you will get a feel of the process. The presence of the colorant after the above processing does not indicate that we have not restored the record. Thes records either vintage or new will leach forever. Even in pressings from the same manufacturer, different titles will show different reactions. Not to worry Further, many new records sold as new are not in fact new, but repacks, complicating at times the restoration effort and understanding process times.
NO: If you play the record often, once every two years apply surfactant at 12, 4 and 8 o’clock positions on the record and then insert the record back into the machine for one 5 minute cycle. Then dry and polish as usual. This as you have handled the record and where fingerprint oils have been applied to the record's edges due to normal record handling. Then do use the goat hair brush with a mist of surfactant applied to a spinning record on a turntable to polish.
TO PLAY: Take the record out of its non PVC, HDPE, non paper sleeve, place on the turntable mat, then use both the felt then the carbon fiber brush to remove dust, then static, then play. (We supply PVC free, anti-static, anti-fungal record sleeves.)
When playing any record, restored or not: Take the record out of the sleeve, set the record on the turntable mat, spin the record. Using our combination carbon fiber and parastatic felt brush, use the felt brush to first remove dust from the record’s surface, then use the carbon fiber side to remove finer dust in the grooves as well as to remove static before playing the record. Play the record. Then return the record to its sleeve. If your turntable is equipped with a cover, close the cover. This reduces dust from being attracted to the record as it spins and landing on the grooves. Also reduces static “charging” of the record. The cover also reduces the cartridge from picking up reflections of sound from the speaker depending on where the turntable is located.
Many points: 1) Using distilled water I am assuming in a tank alone will not see ANY ultrasonic do much as vinyl PVC repels water. 2) When the sonic microbubbles collapse, the resulting wave created by cavitation will not do much to clean the grooves. This as where records that are spaced at ½” or less than 1.78" apart sees the microbubbles implode before rising, due to the creation of standing waves, thus the system does not see the ultrasonic cavitation access all the grooves up to the dead wax area. As proof where only 4 records may be processed in a 6 liter tank; USE THE ALUMINUM FOIL TEST that we have shown in the Audiophile Society of NJ Zoom presentation that you may access on our first page. 3) With records now spaced apart at as distance unknown as we do not know the configuration of the sonic transducers, brushing in our surfactant in the grooves will assist in cleaning your grooves, BUT IN FACT at the same time will accelerate the damage, as now the 40 KHz in the areas of the wave hitting the record via cavitation will now see the 40 KHz wave of the machine you bought from China “sandblast” the grooves. This as aided by our surfactant as a wetting agent that was brushed in the grooves as we have changed the charge of the record to be the opposite of the medium in the tank. 40 KHz or higher on the record. Review our web site for details as how we use a 2D/3D Microscope to study effect and cause. 4) Our system uses safe 35 KHz and where we have designed a system that spaces records correctly which also does not have a heater which will heat water in excess of 105 deg F. . It seems your system has a heater. We strongly dissuade you from using 40KHz with our surfactant applied. I am very sensitive to this. Respectfully stated: Many people read blogs and are not experts.
In our videos and documentation we ask that you look at the rise and then fall of the “whitish like materials” that comes out of the grooves when we brush our surfactant into the grooves in subsequent 5 minute cycles. This after the second 5 minute cycle using surfactant. We recommend for new records one uses 3 or 4 five minute cycles on the record. In your situation the white “fluff” or residue that appears on your needle is the softened contaminants that the process has started to loosen from the grooves. Now dislodged by the needle. Try another 3 five minute cycles. Watch for the rise and fall of the whitish materials that the goat hair brush picks up when new surfactant is applied and is brushed in. The reduction or quick evaporation indicates to you the last 5 minute cycle before drying
PVC (vinyl) repels water.
When we apply a surfactant onto the record as well as into the grooves of the record by way of our goat hair brush and then subject the record to a 2 or 5 minute cycle, as we approach the 5 minute point, all of the surfactant has already been removed by the ultrasonic cavitation process.
Keeping the record in the machine for another 10 minutes will not see any significant improvement as where there is no longer any surfactant in the record’s grooves.
The purpose of this ionizing agent we supply is to change the relative charge of the record with respect to the distilled water in the tank. We need to attract the plasma wave to brush against the surfactant and get into the groove.
Repeated cycles are therefore needed as discussed earlier.
Using our surfactant with sonics that are 40 KHz and higher will see records damaged due to this ionizing effect and the excessive speed of the plasma wave their systems generate.
At our 35KHz, we create a safe wave for both vinyl as well as shellacked/lacquered records.
The oldest method for production of pure water is the thermal method or distillation. Distilled water is water that has been purged of impurities by evaporating it through boiling and then letting it re-condense elsewhere. This is the most natural form. When water evaporates, all the non-volatiles dissolved in the water are left behind, though some volatiles will evaporate with the water, such as nearly all minerals, many chemicals, and most bacteria. When the water re-condenses in a different container, the water will be closer to pure H2O. This works not only for minerals but also for neutrally charged organic material, bacteria, and viruses in most cases. Distilled water is not recommended to be used for drinking as it lacks the minerals which can also provide health benefits.
Using electrolysis and or osmosis added as a process, Deionized water is water where the dissolved ions have been removed leaving mostly pure water and is created by mixing the water with an electrically charged resin containing cations, anions, or both. Although this process removes dissolved minerals from the water, it is not effective in removing bacteria, viruses, or non-charged organic molecules.
Since both treatment methods produce high purity water, choosing between deionized water vs. distilled water often depends on how you're using it. Distilled water is often more pure, especially if it's been filtered first, and it should not contain any bacteria or other pathogens which could, in theory, be left in DI water. Distilled water, especially if it's been double or triple distilled, can be used for nearly all laboratory applications, including those in which DI water might not be pure enough. As we are dealing with fungus, and its removal from records, we do not want to use deionized water in any form in our sonic bath/tank.
FYI: There are 2 types of alcohol: 91-99% IPA and 70% IPA. We use the latter diluted to kill fungus in the basin. We do not use it to clean the record as basically vinyl will repel water. We mix 1.4 ounces of this in our system’s tank. Our mix is PVC safe. UNLIKE OTHER SYSTEMS, THIS LOW CONCENTRATION THAT IS PERFECTLY SAFE FOR THE RECORD IS NOT USED FOR CLEANING.IT IS USED TO KILL DORMANT AND LIVE FUNGUS FOUND ON THE RECORD.
While not tied to this, the first cycle performed with our machine does remove light surface grease and fingerprint oils and wet the record. It does not clean the grooves. The brushed in IONIZING surfactant with the ultrasonic does this.
INDEED: Never use a cleaner with alcohol, or a cleaner that does not have an MDS Safety Sheet or clear indication of what is in the cleaner itself as an ingredient(s).
Per the PVC Chemical Compatability Chart: Alcohol will damage some plastics, but not all. Many blogs are not clear as to this. See below… Our chemist confirms by the resin code, or "recycling symbol", found on most plastic items:
Poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET or PETE - PET is not very soluble in ethanol or isopropanol, but prolonged exposure may cause crazing or stiffening due to the dissolution of plasticizers.
High-Density polyethylene, HDPE - HDPE is resistant to most things.
Poly(vinyl chloride), PVC - PVC is not very soluble in ethanol or isopropanol, but prolonged exposure may cause crazing or stiffening.
Low-Density polyethylene, LDPE - LDPE is resistant to most things.
Polypropylene, PP - PP is resistant to most things.
Polystyrene PS - PS is not very soluble in ethanol or isopropanol, but prolonged exposure may cause crazing or stiffening.
Please note where plasticizers come into play. Plasticizers or dispersants are additives used in the base PVC materials of the record that increase the plasticity or fluidity of a material. Plasticizers are added to help maintain flexibility in a plastic. Various phthalates are commonly used for this purpose. Since they are small molecules they may extract or leach out of the plastic causing a loss of flexibility with time. Just as deliberately added small molecules may leach out, small molecules from the environment may be absorbed by the plastic and act like a plasticizer. Compatibility in the Hansen system increases when values of all three forces of solvent closely match the values of solute. Benzyl butyl phthalate has the best match of parameters with PVC and it is known to be the most aggressive plasticizer of PVC. In the case of phthalates, which are used in the manufacture of vinyl records, we see where the longer the hydrocarbon chain of alcohol involved in plasticizer, the worse the match of its parameters and the worse a solvating power of plasticizer. Diisononyl phthalate is close in solvating power to di-(2-ethylhexyl) adipate which is considered as a secondary plasticizer. The length of hydrocarbon chain in alcohol influences critical solvation temperature. In practical terms, less volatile, higher molecular weight plasticizers require increased processing temperature.
All said and told: 91-99% IPA while not detrimental to casual contact with a vinyl record. Only if there is constant prolonged long term contact in also large concentrations is there an issue over extended time. More on this later.
While Alcohol in its unconcentrated form is a good degreaser, we recommend only 1.4 US oz of 70% IPA to 228 US ounces of distilled water. Very diluted. We have taken much time study to determine what is minimally needed. Our purpose is to kill fungus, either live or dormant that will end up in the sonic's basin.
As to fungus and where 70% made outside of a dilution:
QUOTE: 70% Isopropyl Alcohol: Between the concentrations of 60% and 90%, Isopropyl alcohol is a very effective agent against microbial bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Higher concentrations don’t generate a much more desirable effectiveness against bacteria, fungi and viruses. This is because, there has to be a significant enough presence of water with the Isopropyl alcohol in order to be effective. And this percentage of water needs to be at least more than 10% within the solution. And the mixture of 30% water with 70% Isopropyl alcohol works best. The reason water is so important is because it acts as a catalyst and has a major role in denaturing the proteins of cell membranes of vegetative cells. 70% IPA solutions are very effective in breaching the cell wall fully. Also, the presence of water slows down evaporation and increases the surface contact time with the membrane. With 91% IPA, the evaporation is instant and protein coagulates, rendering the effect of the IPA greatly reduced.
This means that 91% IPA takes a greater time to act and doesn’t kill as much bacteria as 70% IPA. The latter is also cheaper.
Also all alcohols evaporate, 4 hrs. average for 70%. Much faster for others of higher concentrations (99%)..
The issue is the plasticizer and where we are compatible as a water soluble alcohol.
Before using any cleaning agent or chemical on a record's surface, consult the PVC CHEMICAL COMPATABILITY CHART. An example: http://www.ipexna.com/media/1588/pvc-chemical-resistance-guide.pdf
TO SAFE CLEANING: Many end users do not check the compatibility of the products they are using with their records. Records are made with PVC and have added to the mix liquefiers, plasticizers, stabilizers and the like. With this in mind, first and foremost, many available cleaning products for vinyl records do not list their ingredients to aid first responders in a medical emergency when product ingestion is involved. Secondly: Never use a product on your precious records if you do not know the compatibility of the cleaner with PVC, this as we have discovered where many ingredients affect PVC negatively. Third: Never make your own mix without referring to a PVC CHEMICAL RESISTANCE GUIDE. (one suggested link: http://www.ipexna.com/media/1588/pvc-chemical-resistance-guide.pdf ).
To respond to many using chemicals such as Tergitol(R) recommended by many in making their own mix, as described by the manufacturer, (Dow Chemical), it is described as a Secondary Alcohol Ethoxylate Surfactant and while it is considered as an excellent emulsifier & detergent by the manufacturer in the wetting of surfaces that are essential for many surfactant applications, the manufacturer remarks where it can also be used as a paint thickener and aids in rinse-ability of solvent-based systems. This product as suggested by the manufacturer is to be used as a solvent and to use in cleaners, prewash spotters and paints & coatings. As classified by California Proposition 65 per the manufacturer's MDS, it is listed as Ethylene Oxide by Law.
(Proposition 65, officially known as the California Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986 protects the state's drinking water sources from being contaminated with chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm, and requires businesses to inform Californians about exposures to such chemicals and requires the state to maintain and update a list of chemicals known to the state to cause cancer or reproductive toxicity.)
Per the State: Tergitol (R) is made of of Ethylene Oxide and alcohols forming a Polyethylene Glycol Trimethylnonyl Etheand and Polyethylene Glycol Dinonylphenyl Polyoxyethylene and as such it raises health concerns. Stated by the Manufacturer: May cause eye irritation; May be harmful if inhaled; Causes respiratory tract irritation and may be harmful if absorbed through skin and causes skin irritation. May be harmful if swallowed. (This from the Dow Chemical MDS Sheet.) Referring to the PVC Compatibility chart, Ethylene Oxide is not favorable to PVC. So one needs to consider how any chemical or product used in cleaning or processing PVC records is selected for PVC compatibility and health reasons. Advice: never make your own solution, always ask for the composition of the cleaner that you are buying. Check the Chart!
As the ultrasonic sees the micro-bubbles cavitate and implode creating a 900 KPH (500 MPH) wave that hits the record and washes the grooves with the surfactant/wetting agent brushed into the grooves of the record, this ultrasonic action generates kinetic energy and creates heat. As you restore more records and run the machine, over time, the distilled water in the bath heats up. The colored bar underneath the timer shows one the progression of the heating of the water by this released energy. The bar moves left to right. When the machine starts with room temperature and temperate water, the green or green and orange lights are lit. As the system is used, temperature increases, and when it reaches approximately 90 def F (32 deg C), the long red bar lights up. This is normal. No issues for using the system to restore your records. When the water reaches approx. 94 deg F (34 deg C), the small red light to the right of the long red bar lights up. This indicates to your where you have two, three or four 5 minute cleaning cycles left. This before the same small red light to the right of the long red bar lights up and flashes. This indicates to you where you now have reached 105 deg F. (40 deg C.) At this point you need to take any records out of the machine and turn the machine power off, remove the record cover assembly , and let the water in the tank stand and to cool down. We do not want you to clean records at this temperature. Removing the cover speeds up the cooling process. In about 10 minutes of rest and you may start once more. Replace the cover, turn on the main power. To note: At 110-115 deg F, (43 - 45 deg C), this will affect your records. The small red flashing light indicates 104 deg F (40 deg C.) and where we provide you with a margin of safety. Once repowered: It is OK to restart and restore records once more with the long red bar lit. It is safe. Also if you are running the machine non-stop and continuously, turn the machine off every 35 minutes and remove the cover, this to cool down the ultrasonic transducers.
Yes. When you apply our surfactant on the coated record you will in fact see hundred or thousands of small waster droplets appear on the record’s surface. This confirms where a coating has been applied as the coating repels water. This coating makes it more difficult for our process to actually clean the grooves as we have to first remove this coating that is hindering our process. We suggest where you change the method used: brush in the surfactant and just a 2 minute cycle instead of a 5 minute cycle. Keep the record in the machine for only 2 minutes. This as the coating will see the surfactant removed very quickly. Repeat the 2 minute process until you then see the rise and fall of the white paste appearing or its quick evaporation. It usually this takes 9 two minute cycles to restore a coated record.
Thank you for your question. Noted where one 120 KHz system is not even an ultrasonic, rather an ultrasonic bubbler as the machine tested fails the aluminum foil test and cavitation is not measured by a cavitation meter. To your note: The KirmussAudio Model KA-RC-1 revolutionizes the way we take care of records. Need to provide you with some more details ahead of my answer. So: WE ARE NOT A RECORD SURFACE CLEANER, BUT A TRUE ULTRASONIC TECHNOLOGY RECORD GROOVE RESTORATION SYSTEM that over multiple 2 or 5 minutes cycles processes 4 records at a time, first removing films from past cleaning methods, whether manual, vacuum or ultrasonic, and then removes the release agent from the pressing plant that holds the dust particles that are micro welded into the grooves that cause those unexpected and unwanted pops heard when playing a new record. TO OUR DIFFERENCE: Water and Plastic repel each other, they have the same charge, so unless one changes the charge of the record as we do, our system also would not be effective either. Therefore the application of the ionizing spray over several cycles as the charge dissipates as the record spins. With the release agent no removed, one will no longer further micro weld dust that is around one’s turntable creating more pops as the release agent which gets heated by the dyne of the needle onto the record is no longer present to be heard. Also where the needle now makes contact with the details of the stamper. SO YOU EXPERIENCED THIS IN TESTING OUR SYSTEM.
So:
To design and our difference, we need to understand the material we are trying to clean (restore). A soft, vinyl or shellacked record. Not going into all the science, we have a groove width from 6 to 48 microns, going from bottom of the groove to the top. We have dust particles, dirst etc that are 3 to 5 microns in size. 35 KHz is known to be the best frequency to select. Dust, durst, surface fungus, paper fibers are 3 to 5 microns in size... THEY ARE NOT SUB MICROSCOPIC (below 0.1 microns), not touched or heard by the needle/pre-amp, so 120 KHz does little. Thus: The KA-RC-1 is a 35 KHz ultrasonic using a 70KHz resonance to even out the distribution of the benefits of cavitation evenly throughout the water medium in the tank so as not to mark the record with unevenly distributed high energy waves in concentrated areas.
To handle multiple sized records safely, a Patented and Patents Pending record suspension system assures where records of any speed and size see their grooves contacted completely up to the dead wax area with the distilled water in the basin. Added where damage to the record and label by mechanical intrusion of skewers and spacers and the like are thus avoided. To processing more than one record: In the Kirmuss design it was noted where the spacing between records is critical and therefore can only process 4 records at a time in a 6 liter tank. (If an additional slot was introduced to accommodate a 5th record, this would cancel the effect of cavitation as proven by the aluminum foil test. (see the Zoom of the Audiophile Society of NJ on our main page showing the results of the foil test on other machines as to record spacing and effects of cavitation.))
To understand what a commercial ultrasonic should do in processing a record: The Kirmuss process does not use a cleaning agent or solution in the basin, as both the record and distilled water in the basin with or without the use of a solvent sees the same electrical charge. As we all know from elementary school science, like charges repel, and that is why all ultrasonics may not remove the release agent or clean adequately records. The Kirmuss process uses an ionizing agent that is applied to the record before insertion into the machine that changes the charge of the record to be opposite to that of the water that is in the stainless steel basin of the machine. (water with or without the addition of a solvent or cleaning solution have the same change as the record). As the induced charge applied to the record now opposite to that of water wears off after 3 or 4 minutes as the record spins, that is why one needs to re-apply the ionizing agent to the record over several cycles. Charging the record once more. The change of charge and potential difference attracts the 35 KHz wave created by cavitation. Thus: the first cycle in the machine removes films from prior cleanings and fungus as well as the majority of fingerprint oils. Then subsequent cycles removes the release agent and micro welded dust from the grooves.
SO: If someone wishes to surface clean the record quickly, and not restore it and removing the release agent from the time of pressing, then only one 5 minute cycle with the ionizing agent applied is required.
To protect the user of the system , we add to the distilled water a maximum of 40 mL ( 1.4 oz) of 70% IPA which while it may assist in degreasing the record from fingerprint oils in the first cycle, the addition of this low concentration of alcohol deemed safe for records is designed to kill live or dormant fungus that comes off of the record while being processed.
As to 120 KHz and 40 KHz ultrasonics, many are NOT ULTRASONICS AND DO NOT USE CAVITATION. THAT IS WHAT YOU EXPERIENCED FIRST HAND. If you are referring to an advertised German 40KHz, Chinese made 40 KHz system, or a European made 120 KHz system: using the universal aluminum foil test, they are ultrasonic bubblers! Agitating water and soap in the basin. Limited to surface cleaning at best. (As to the aluminum foil test used by professional sonic manufacturers to ensure that the transducers used are working); For the German machine we had to remove the 4 felt scrubbers in the machine as they would have torn apart and destroyed our aluminum foil record that we made.)
As a summation: The process of applying the ionizing spray attracts the wave created by cavitation to the record, as the charge of the record is now opposite to that of water. Using the aluminum foil test proves where spacing between records is critical and as such where we are limited by way of physics where we can process only 4 records simultaneously in a 6 liter tank based system. (This is not your case as the machines you described handle only one record at a time.)
As to determining when a record is clean and restored, our process allows you to see this first hand as the ionizing surfactant agent that is applied over several cycles and as it is brushed onto the record between cycles, one may witness at first an increase and then a subsequent decrease in the appearance of a toothpaste-like substance between cycles on the record's surface, materials that are being brought up by the goat hair brush. This material brought up is what the ultrasonic softened in the previous cycle. A decrease/rapid evaporation signals that the cycle is finished. UNLIKE YOUR SYSTEMS where the instructions ask you to repeat cycles blindly if you are not satisfied: This intentional cyclic process validates the effectiveness of the system: removing fungus, contaminants, as well as agents applied in prior cleaning methods left as films on the record’s surface, and finally the release agent itself that only our system may remove.
As top why we do not use air or vacuum drying: There is no need for air or vacuum drying as restored records come out virtually dry. Any remaining water droplets are removed by the supplied optician’s cloth.
New records see gain of 1.3 dB over floor, and records of unknown provenance see a gain between 3 and 4 dB.
Hope this wordy response provides you with details as to why we differ.
As you still may have your 120 KHz machine, before returning it and buying ours, you may want to make an aluminum foil record to prove that the sonic sold you is not a sonic, rather a bubbler. That is why you heard the results of our record restoration system processing the previously cleaned record using your 120 KHz system.


